Kenya partners with WHO to tighten tobacco control, review existing laws

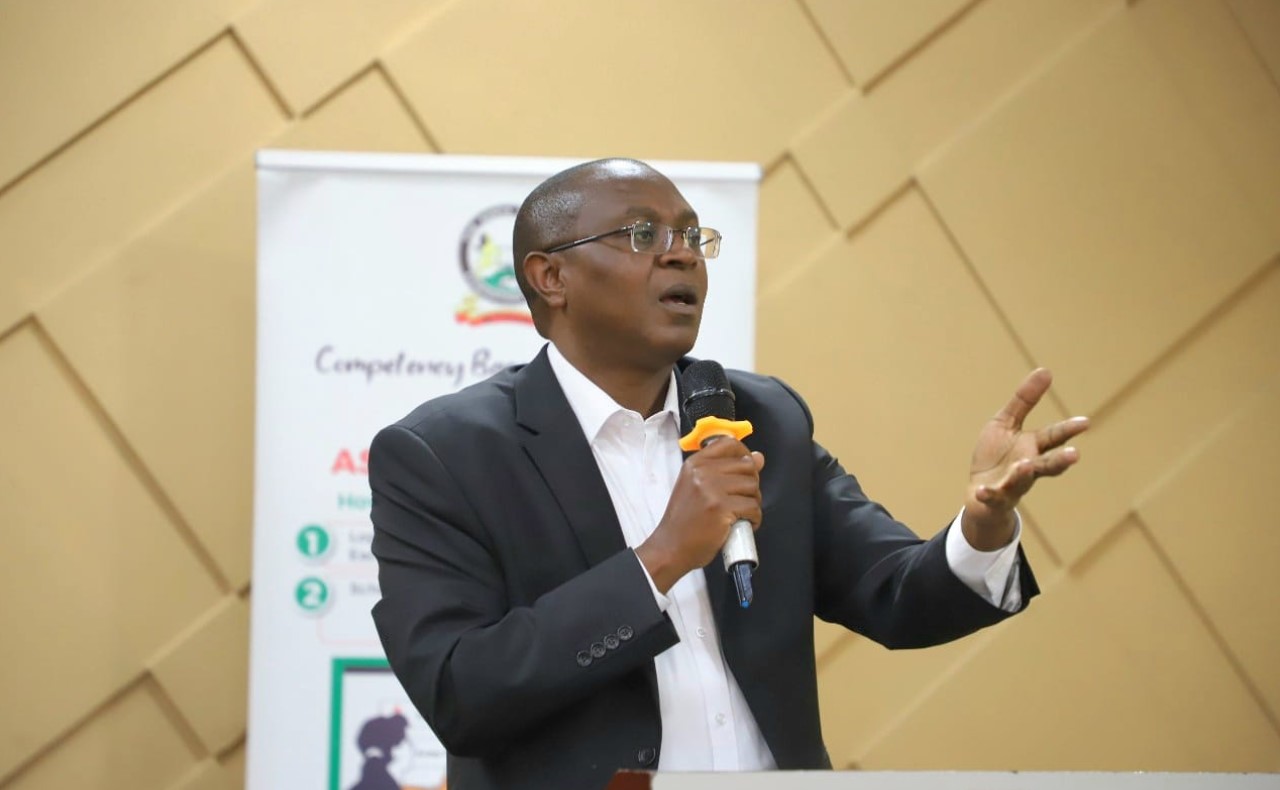
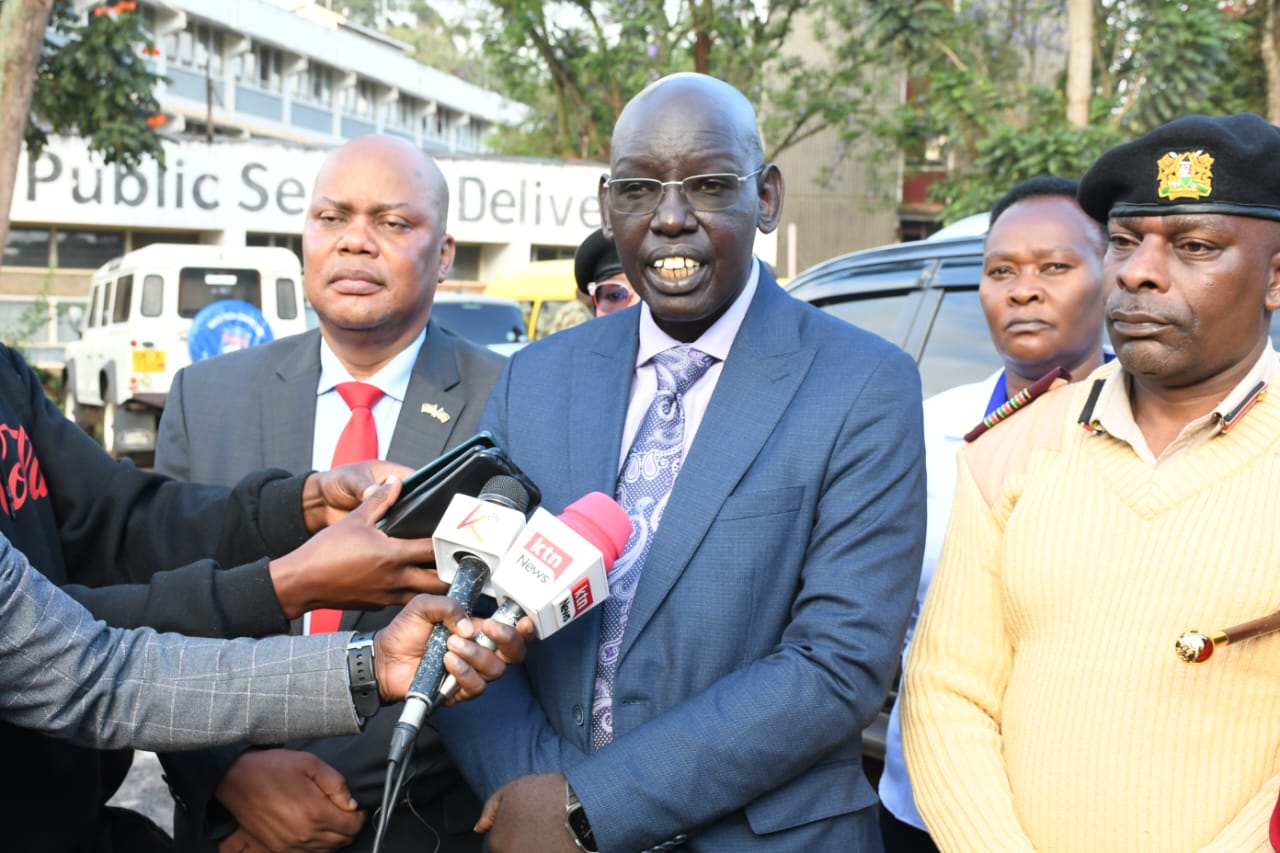
Health Cabinet Secretary Aden Duale said the partnership will help advance the country’s efforts to reduce tobacco-related harm by updating its legal framework to better govern the production, sale, advertising, and consumption of tobacco products.
Kenya has partnered with the World Health Organisation (WHO) to strengthen its national response to the escalating health risks posed by tobacco use.
As part of the collaboration, WHO will provide technical expertise to support the review and modernisation of Kenya’s Tobacco Control Act, ensuring alignment with global health standards.
More To Read
- Calls for safety awareness as world marks Drowning Prevention Day
- Committee proposes establishment of national deceased organ donation programme
- CS Duale orders security audits at all referral hospitals after KNH patient murder
- Vegetable intake low in Kenya amid growing health concerns
- Kenya vaccinates over 21 million children against typhoid, measles
- Sharp decline in childhood vaccinations leaves 133,000 children unprotected – report
Health Cabinet Secretary Aden Duale said the partnership will help advance the country’s efforts to reduce tobacco-related harm by updating its legal framework to better govern the production, sale, advertising, and consumption of tobacco products.
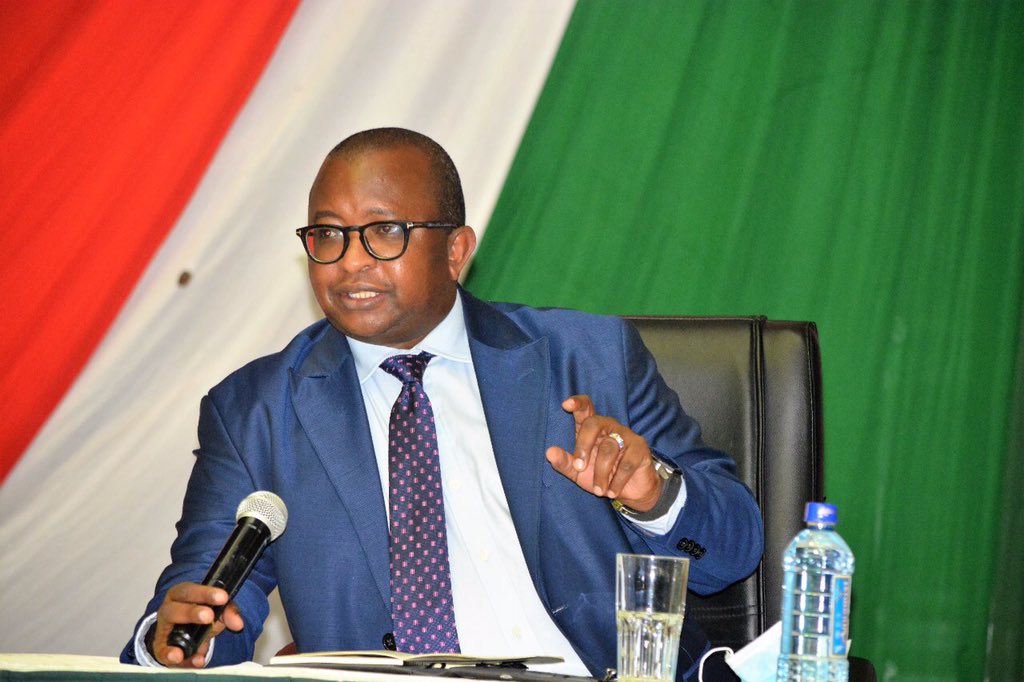
“These amendments aim to modernise Kenya’s legal framework to more effectively govern the production, sale, advertising, and consumption of tobacco products,” Duale said during a bilateral meeting with WHO officials held at Afya House, Nairobi.
The discussions focused on mechanisms to track the proposed amendments to the Tobacco Control Bill, which forms part of Kenya’s broader effort to curb tobacco use and mitigate its impact on public health.
WHO, in turn, reaffirmed its support for strengthening national laboratory capacity for the independent verification of tobacco products.
Today, the Ministry of Health, in collaboration with the World Health Organization Kenya Office, held a high-level dialogue to advance Kenya’s tobacco control efforts.
— Mary Muthoni Muriuki, CBS, HSC (@psmuthoni) June 10, 2025
The meeting, presided over by Health Cabinet Secretary Hon. Aden Duale, brought together key stakeholders to… pic.twitter.com/WPjts0SGRo
Duale briefed the WHO delegation on Kenya’s ongoing progress in tobacco control, citing the successful transition of more than 9,000 farmers from tobacco to alternative crops such as high-iron beans. He requested WHO’s support in initiating a structured review of the Tobacco Control Act (2007) and its associated regulations.
He further called for collaboration in scaling up enforcement efforts at the county level. These include the introduction of updated inspection protocols, building local capacity, enhancing cessation services, and integrating tobacco control into the Ministry’s expanding digital health superhighway.
Reaffirming Kenya’s commitment to the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC), Duale emphasised that the government has a constitutional obligation to protect the right to the highest attainable standard of health.
Other Topics To Read
Top Stories Today