Health

Antenatal clinic attendance in Kenya has dropped from 98 per cent to 62 per cent in four years, fuelling preventable maternal complications, newborn deaths and stillbirths as conditions like anaemia and pre-eclampsia go undetected.
The suspension applies specifically to any component of the deal involving the transmission or handling of personal health, epidemiological or other sensitive medical data.
The World Malaria Report 2025 warns that failure to address resistance could reverse years of progress in reducing infections and deaths across the country.
The National Treasury has been directed to disburse all personnel emolument costs to county governments by the third day of every month.
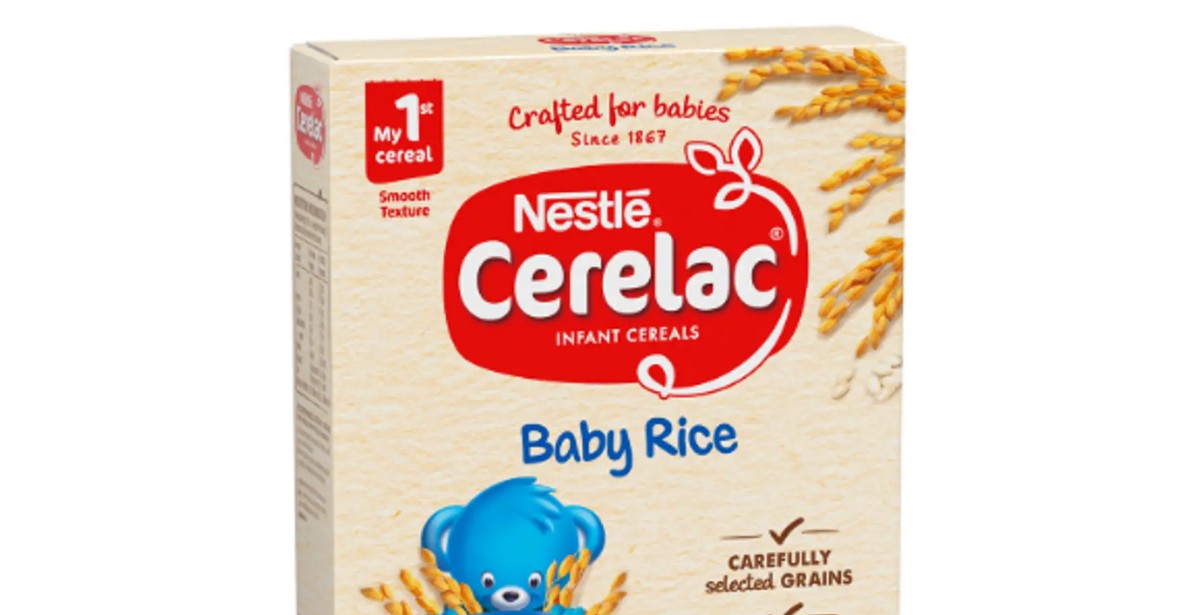

An investigation finds Cerelac baby cereals sold in Kenya and across Africa contain high levels of added sugar, unlike European versions, raising public health concerns and prompting calls for Nestlé to reformulate.
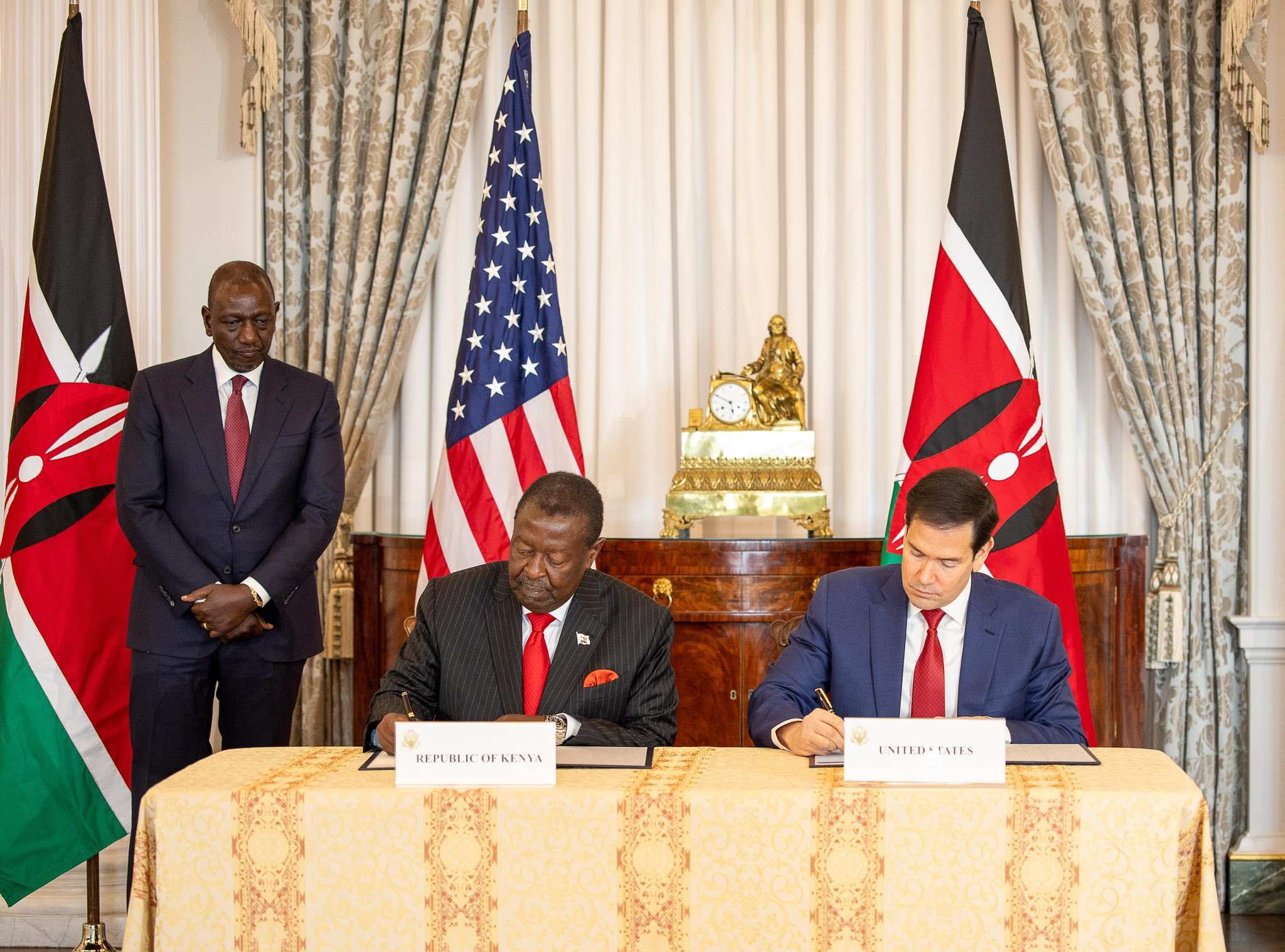

Omtatah claims the deal, said to commit Sh323billion to Kenya's health sector, was concluded without public participation, parliamentary scrutiny, or disclosure of its full contents.

The decision also directs the development of a framework to transition Community Health Extension Workers (CHEs) to permanent and pensionable terms.

KNH has repeatedly faced difficulties with its Linear Accelerator (Linac) machines, which are essential for administering precise radiotherapy.

The WHO recommends that healthcare providers give focused guidance on quitting to anyone planning or attempting pregnancy.

Duale said the government has largely met welfare commitments and only final steps remain.

The study looked at 17 areas, including maternal health services, family planning, caregiver practices, and child health and nutrition. Key results showed that more women started antenatal care early, up 5 per cent, more gave birth in health facilities, up 7.3 per cent and with skilled professionals, up 7.9 per cent.

The illness spreads through close contact with an infected person, including sexual contact, and can also be passed on through coughing or sneezing. It typically begins with flu-like symptoms such as chills, body aches, and fatigue, followed by a rash that may develop into blisters.

Global leaders and philanthropists have pledged $1.9 billion at an Abu Dhabi summit to support polio eradication, aiming to vaccinate 370 million children annually and strengthen health systems worldwide.

A University of Arizona study links PFAS-contaminated well water to higher risks of low birth weight, preterm birth and infant mortality, underscoring long-term health and economic impacts in the US and beyond.

KNCHR warns many Kenyans remain locked out of healthcare despite a Sh138.1 billion health budget and the SHA scheme, citing detained patients, low enrolment and gaps affecting vulnerable groups.

A Lancet series and WHO warn that rising ultra-processed food consumption is fuelling non-communicable diseases worldwide, with growing impacts in Kenya and widening health inequalities.

Nigeria’s President Bola Tinubu confirms troops were sent to Benin at the government’s request after a failed coup, as ECOWAS deploys a regional force to help preserve constitutional order.

Kenyan MPs have invited bids for private medical insurance for themselves and their families, bypassing the SHIF scheme they publicly praised, raising questions over leadership and use of public funds.

The Health Ministry is urging stronger regional cooperation to tackle rising disease and safety risks along East Africa’s busiest transport corridors, warning that growing mobility is amplifying cross-border health threats.

Kenya registered 4,186,000 cases in 2025, up from 3,294,000 in 2024, an additional 892,000 infections.
WHO and the World Bank report 1.6 billion people pushed deeper into poverty by health costs and 4.6 billion lacking essential services, as Kenya and other nations struggle to meet UHC goals.

Duale said the framework strictly protects citizens’ privacy and focuses only on aggregate-level data, ensuring no individual medical records or identifiers are shared.

The Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) said it has recorded 432 suspected incidents between July and September 2025, with the majority involving adults aged 18–64 years.

The Public Service Commission has extended for six months the temporary deployment of over 1,400 former NHIF staff to the Social Health Authority, amid delayed recruitment and ongoing concerns over SHA services.
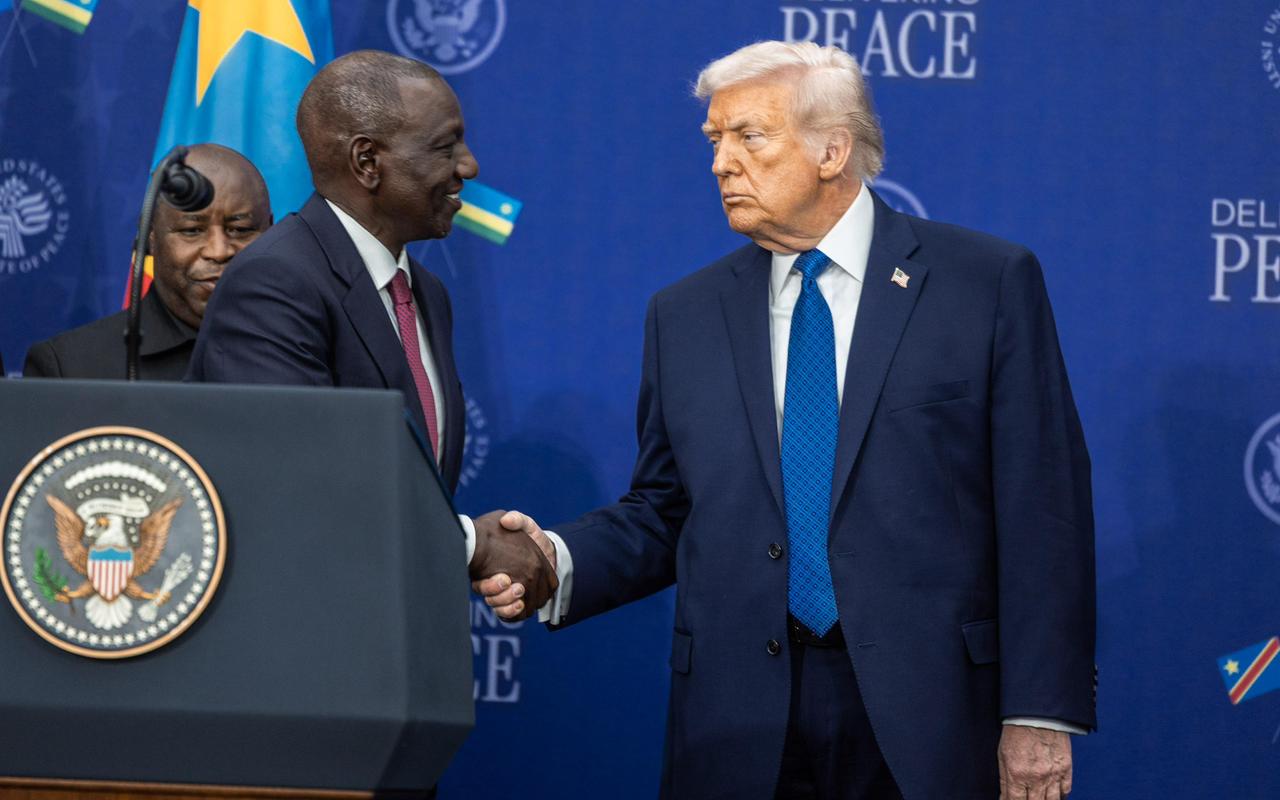

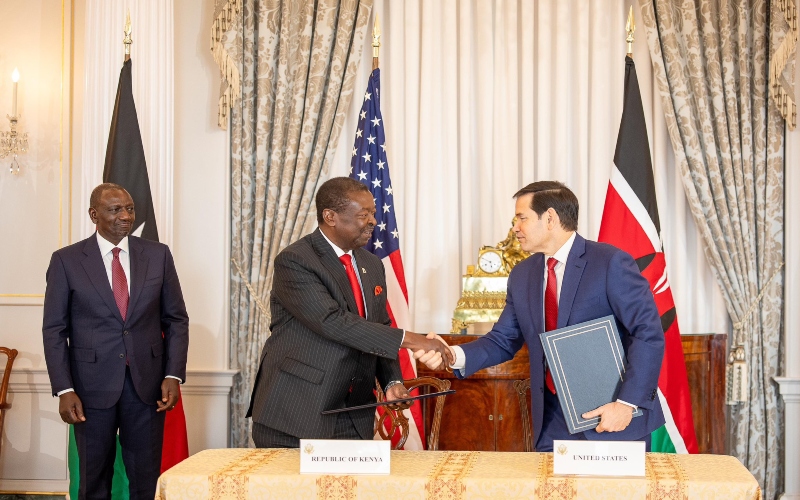
Ruto witnessed the signing of a landmark agreement with the United States, securing a US$1.6 billion (Sh208 billion) investment in Kenya’s health sector over the next five years.

At the forum, an additional 15 National Health Compacts, country-led, five-year reform plans that align health and finance institutions behind measurable goals, were introduced.
Researchers analysing about 500,000 GLP-1 users report a 12% higher risk of chronic cough, possibly via worsened acid reflux. The findings matter as Ozempic and Wegovy use grows worldwide.

A Nairobi mother’s story highlights hidden hunger, where families eat enough to feel full but lack vital nutrients, raising risks of anaemia, poor growth and obesity as food costs and urban diets shift.

Parliament’s Health Committee has approved a Bill to criminalise detaining patients or bodies over unpaid medical bills in Kenya, imposing fines and jail terms while requiring lawful debt recovery.

Kenyan senators have tabled a motion urging the Health Ministry to build and equip national teaching and referral hospitals in all regions, arguing that overreliance on Nairobi facilities leads to preventable deaths.

Parliament’s Justice Committee has backed a bill to scrap Kenya’s law criminalising suicide attempts, urging a shift to health-based care and stronger mental health services nationwide.

Under the deal, the United States will provide US$1.6 billion (Sh208 billion) over five years, while Kenya will contribute approximately US$850 million (Sh110.04 billion) from domestic resources.

Kenya and the US have signed a Sh220 billion health cooperation and data sharing deal. Officials say only anonymised, aggregated data will be shared under Kenyan law, aiming for a self-reliant health system.

Kenya and the US have signed a $1.6 billion Health Cooperation Framework, directing funds to Kenyan state health institutions to bolster universal coverage, infrastructure and emergency preparedness over five years.

Kenyan climate and health agencies forecast no malaria epidemics in Kakamega, Kisii and Nandi for December 2025–January 2026, citing low rainfall and higher temperatures that limit mosquito breeding.

The Gates Foundation warns child deaths under five are set to rise for the first time this century as global health funding falls, threatening hard-won gains against preventable diseases.
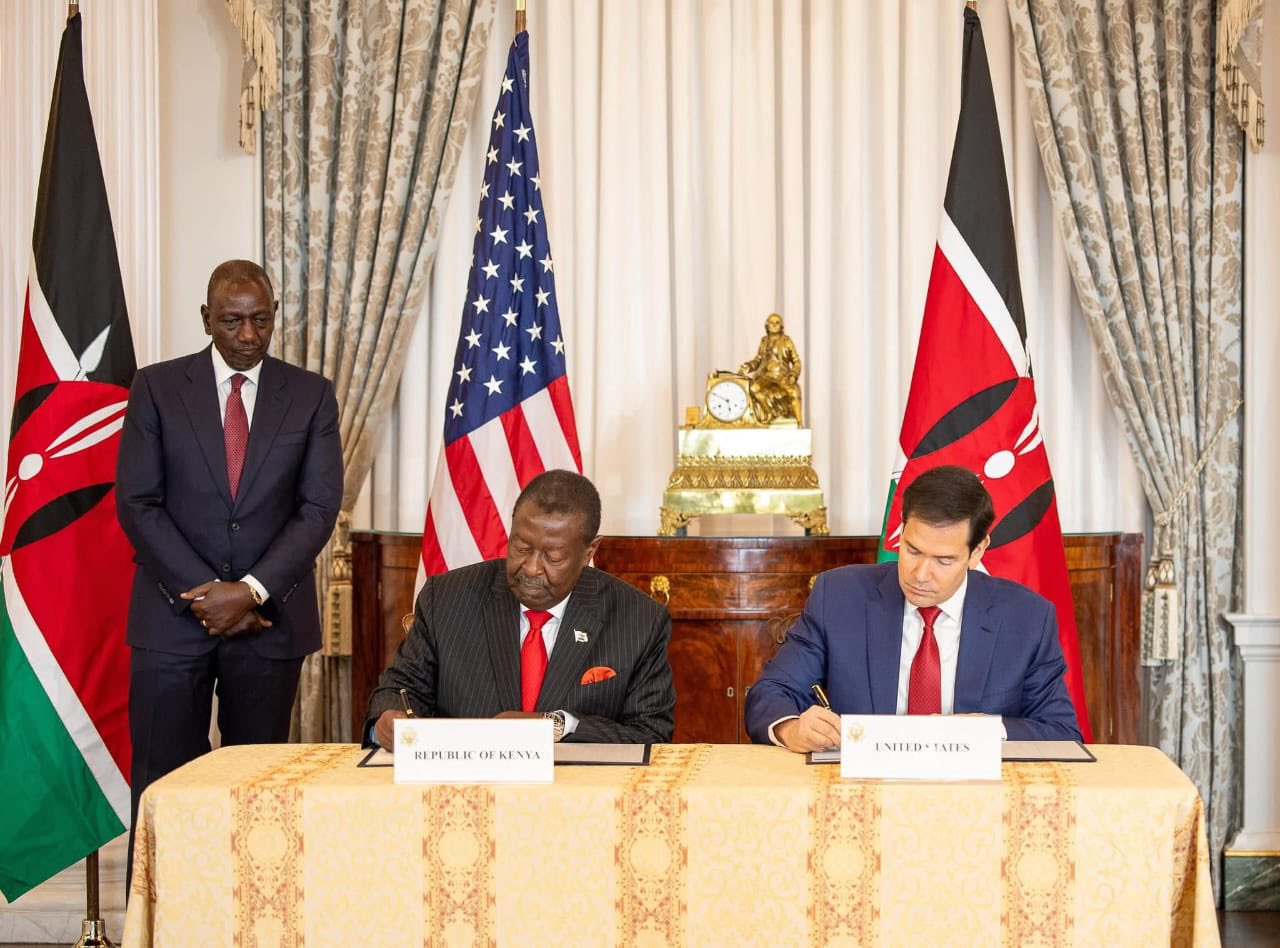

The agreement is the result of months of high-level negotiations, beginning on August 27, 2025, and establishes Kenya as the first African country to secure a new health cooperation model with the United States.
The WHO’s latest annual update shows impressive progress since 2000: intervention has saved an estimated 14 million lives worldwide over the last quarter of a century, and 47 countries are certified malaria-free.
A study of over 280,000 older adults in Wales found the shingles vaccine was linked to a 20 per cent lower dementia risk and improved survival in people already diagnosed.
The implications of this finding are significant. Because the bacterium is resistant to many antibiotics, including some of the strongest available, treating infections caused by it becomes much more difficult and, in some cases, nearly impossible.

A new WHO report finds rising malaria drug and insecticide resistance, 282 million cases and 610,000 deaths in 2024, even as vaccines and new tools avert 1 million deaths worldwide.

A large study of over 10,000 adolescents links smartphone ownership before age 12 to higher risks of depression, poor sleep and obesity, raising concerns for parents and caregivers.

The Senate is seeking public views on the Autism Management Bill, 2025, which proposes a national framework for early detection, care and data on autism across Kenya’s national and county levels.

A Senate committee has proposed restructuring KEMSA and other state corporations into executive agencies to clarify national-county roles, curb funding disputes and streamline devolved services across key sectors.

A KHRC report says Kenya now spends 68% of ordinary revenue on debt and wages, breaching legal limits and shrinking funds for health, social protection and development projects.
New data from African trials and global studies show long-acting HIV injections can match daily pills for viral suppression and prevention, with fewer doses and potential benefits for stigma and adherence.

The committee, chaired by Seme MP James Nyikal, noted that reimbursements under SHA have been inconsistent, with some facilities recording no disbursements at all.

A new Kenyan Bill proposes fines of up to Sh10 million and 10-year jail terms for unauthorised organ removal, creates a national regulator and follows a probe into alleged trafficking at Mediheal Hospital.

A JAMA Neurology study of over 11 million US veterans finds untreated obstructive sleep apnea is linked to higher Parkinson’s disease risk, with early CPAP treatment appearing to reduce that risk.

The WHO has issued conditional guidance supporting GLP-1 drugs for adult obesity, alongside lifestyle counselling, marking a shift in global treatment strategy and raising questions on access, safety and cost.

Two large studies suggest that untreated or persistent maternal thyroid imbalance during pregnancy is linked to higher autism risk in children, underscoring the importance of monitoring thyroid health in expectant mothers.

A National Assembly Health Committee report finds unpaid claims, IT outages, and governance gaps are undermining Kenya’s Social Health Authority and straining hospital finances nationwide.
Trending