Kenya confirms outbreak of Mpox
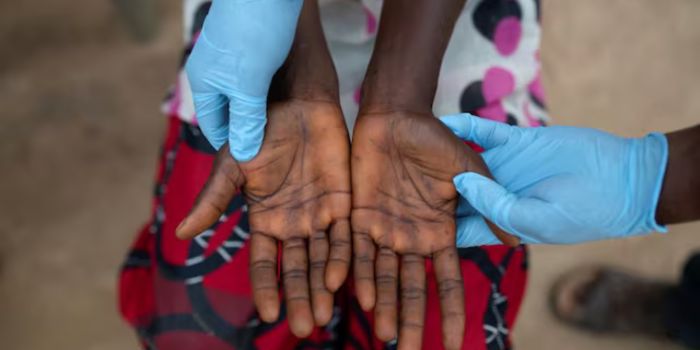
According to the Ministry of Health, the case is from an individual travelling from Uganda to Rwanda through Kenya.
The Ministry of Health has confirmed an outbreak of Mpox in Kenya at the Taita Taveta one-stop border point.
According to the Ministry of Health, the case is from an individual travelling from Uganda to Rwanda through Kenya.
More To Read
- Mpox deaths near 2,000 in Africa since 2024 amid recent decline in cases: Africa CDC
- Health authorities launch 10-day mpox vaccination drive at Malaba border
- Africa: A tentative start in mass vaccine production
- Mpox outbreak: What you need to know to stay safe
- Rising mpox cases, cholera outbreaks and HIV misinformation straining Kenya's public health sector- report
- 314 mpox cases confirmed as MoH ramps up containment across 22 counties
The East African Community (EAC) had earlier issued a critical alert to its member states, urging them to educate their populations on the prevention and control of Mpox (monkeypox), an infectious disease that has recently seen a resurgence in the region.
This call to action follows alarming reports from the World Health Organisation (WHO) regarding outbreaks in Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
The EAC released a statement from its Arusha headquarters, emphasising the severity of the situation, especially in the DRC, where Mpox cases have surged over the past two years.
Mpox is a contagious disease transmitted through direct contact with the bodily fluids or lesions of an infected person. The Ministry is advising the public to remain cautious and alert for symptoms of Mpox, which include fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes.
Kenya is particularly vulnerable due to the high volume of cross-border movement between Kenya and other East African countries.
To manage the outbreak and prevent further transmission, health authorities are implementing several measures. These include heightened monitoring and screening at border points, public health campaigns to raise awareness, and guiding preventive practices.
Travellers and residents are encouraged to maintain good hygiene, avoid close contact with individuals showing symptoms of Mpox, and seek medical attention if they suspect exposure to the virus.
Mpox outbreak in Africa
Mpox cases continue to surge in Africa with a new strain spreading in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Doctors Without Borders (MSF) reports that DRC has recorded over 12,300 suspected cases and 479 deaths in the first half of this year, with the new strain having an estimated death rate of 10 per cent.
Burundi has confirmed three new cases, South Africa has documented 20 cases, including two deaths.
According to the Africa Centre for Disease Control, as of July 28, 2024, a total of 37,583 cases and 1,451 deaths (with a case fatality rate of 3.9 per cent) have been reported across 15 African Union member states: Benin, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic (CAR), Congo, DRC, Egypt, Ghana, Liberia, Morocco, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sudan, and South Africa.
In 2023 alone, there were 14,957 cases and 739 deaths (case fatality rate of 4.9 per cent) reported in seven member states, representing a 78.5 per cent increase in new cases compared to 2022.
In 2024, up to July 28, there have been 14,250 cases (2,745 confirmed and 11,505 suspected) and 456 deaths (case fatality rate of 3.2 per cent) reported from 10 member states: Burundi (8 cases; 0 deaths), Cameroon (35 cases; 2 deaths), CAR (213 cases; 0 deaths), Congo (146 cases; 1 death), DRC (13,791 cases; 450 deaths), Ghana (4 cases; 0 deaths), Liberia (5 cases; 0 deaths), Nigeria (24 cases; 0 deaths), Rwanda (2 cases; 0 deaths), and South Africa (22 cases; 3 deaths).
Other Topics To Read
This reflects a 160 per cent increase in cases and a 19 per cent rise in deaths compared to the same period in 2023. DRC alone accounts for 96.3 per cent of all cases and 97 per cent of all deaths reported this year. Additionally, Chad has reported 24 suspected cases with no confirmed cases this year.
The high movement of people between Kenya and neighbouring East African countries, particularly through major transport corridors, increases the risk of regional spread, as several countries in the area are currently experiencing cases.
The disease primarily affects children under 15 in Africa, while outside Africa, it is more common among men who have sex with men.
CDC recommends that if you develop symptoms of Mpox or have been in close contact with someone who has the disease, consult your healthcare provider about testing and treatment options.
Top Stories Today















































