10 common foods you should never refrigerate: Experts explain why
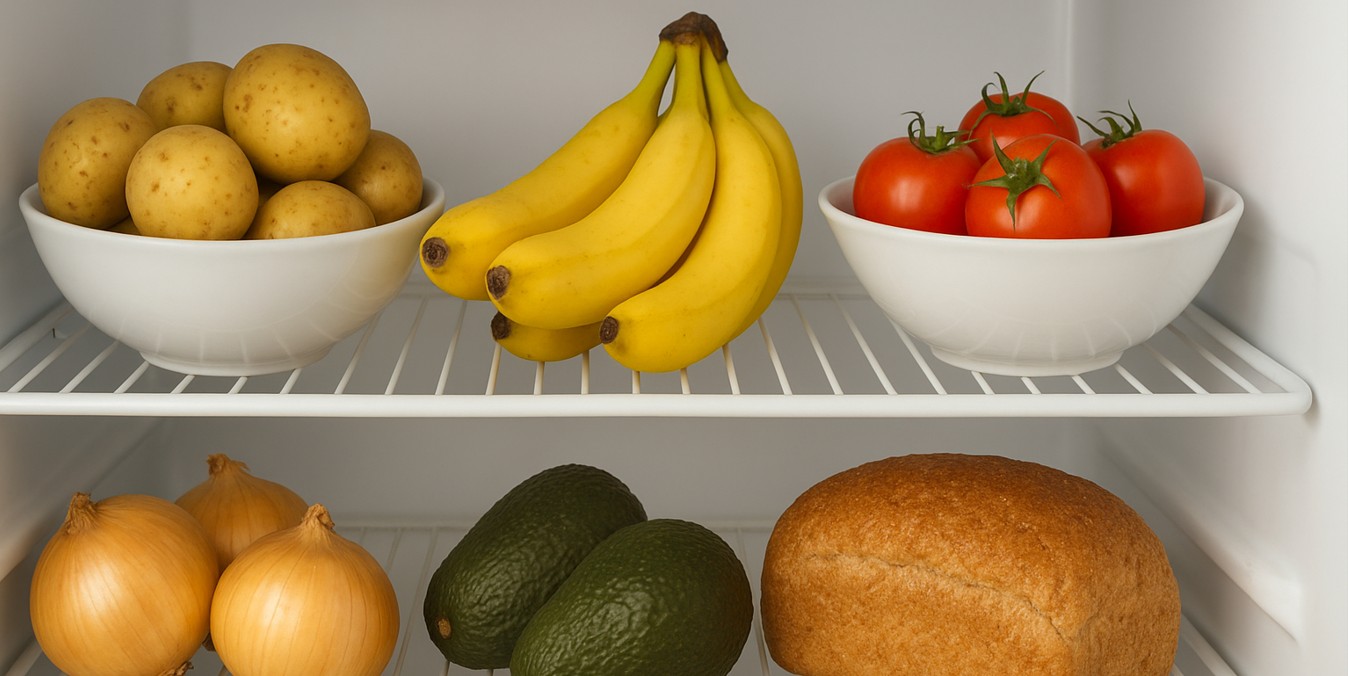

Learn which everyday foods should be stored at room temperature and how refrigeration can ruin their flavour, texture, and freshness.
For decades, refrigeration has been synonymous with food safety and freshness. Many people now use fridges to store almost all types of food.
But not every food benefits from a cold environment. In some cases, refrigeration can alter taste, texture, and nutritional value—or even accelerate spoilage. Experts are now urging consumers to rethink the “fridge-first” mindset.
More To Read
“Many people assume the fridge is always better, but certain foods are naturally adapted to room temperature,” says Dr Jane Mwangi, a nutritionist based in Nairobi.
“Cold can disrupt ripening, enzymatic activity, or moisture balance, which affects both flavour and quality.”
Here are 10 common foods that often fare better outside the fridge:
1. Tomatoes
Refrigeration stops the natural ripening process and damages tomato cell walls, resulting in a mealy texture and reduced flavour. Cold storage also slows the production of volatile compounds responsible for aroma. It is best to store tomatoes at 18–22°C on the counter, away from sunlight.
2. Potatoes
While some people refrigerate potatoes, cold temperatures convert starch into sugar faster, creating a sweet, gritty taste and potentially harmful compounds when cooked at high heat. Store potatoes in a dark, cool (not cold), and ventilated space like a pantry or cupboard.
3. Onions
Whole onions absorb moisture in the fridge, which can lead to softening and mould growth. Their sulphur compounds—the source of their pungency—degrade in humid, cold conditions. Store onions in a dry, open-air spot, away from potatoes.
4. Garlic
Cold encourages garlic to sprout, reducing flavour and introducing bitterness. Garlic prefers a dry, dark environment with good air circulation. Peeled cloves can be briefly refrigerated, but long-term storage is not recommended.
5. Bread
Contrary to popular belief, storing bread in the fridge actually speeds up staling by accelerating starch retrogradation. Cold air also dries it out, affecting texture. Keep bread tightly wrapped at room temperature, or freeze it for longer-term storage.
Other Topics To Read
6. Avocados
Unripe avocados stop ripening in the fridge, becoming hard and flavourless. Only fully ripe avocados should be refrigerated if needed to slow over-ripening.
7. Honey
Honey is naturally antimicrobial and hygroscopic. Cold causes crystallisation and cloudy sediment, which affects spreadability but not safety. Store honey in a sealed jar at room temperature.
8. Coffee
Coffee absorbs odours and moisture in the fridge, which degrades its aroma and taste. Experts recommend storing it in airtight containers in a cool, dark place.
9. Bananas
Cold disrupts ripening enzymes and causes peels to darken prematurely, though the fruit inside remains edible. Keep bananas at room temperature to preserve flavour and appearance.
10. Olive oil
Refrigeration causes olive oil to solidify and lose clarity, affecting usability and flavour perception. When stored in a cool, dark pantry, olive oil retains freshness and nutrients.
While refrigeration slows microbial growth, it can also disrupt enzymatic reactions crucial for flavour and ripening. Foods high in starch, sugar, or natural enzymes often perform better outside the fridge, while perishable items like dairy, meat, and berries benefit from cold storage.
“Proper storage is about balancing safety with quality,” explains Dr. Mwangi.
“Knowing which foods dislike cold helps preserve taste, texture, and nutrients while reducing waste.”
Top Stories Today