Vitamin C boosts skin regeneration and reverses age-related thinning, new study finds
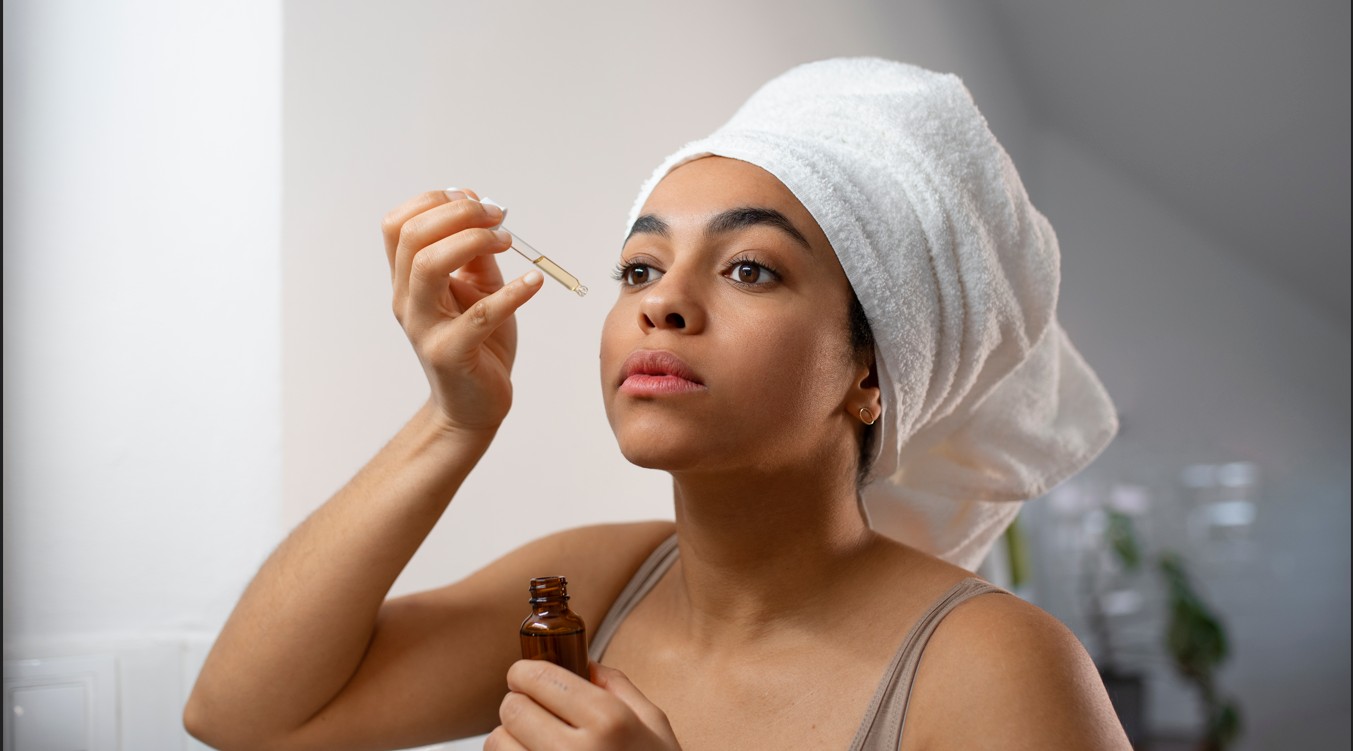

Scientists discovered vitamin C activates key genes that control how skin cells grow, offering a fresh approach to keeping skin strong, resilient, and youthful.
Vitamin C has long been celebrated in skincare for its ability to brighten dull skin and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
However, new research from Japan has uncovered an unexpected benefit: vitamin C can stimulate skin regeneration, thicken the outer layer, and potentially reverse thinning caused by ageing.
In a groundbreaking study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, scientists discovered that vitamin C does not just support skin health; it goes deeper. It activates key genes that control how skin cells grow, offering a fresh approach to keeping skin strong, resilient, and youthful.
Skin, ageing, and a vitamin’s unexpected role
As we age, our skin naturally becomes thinner and more fragile.
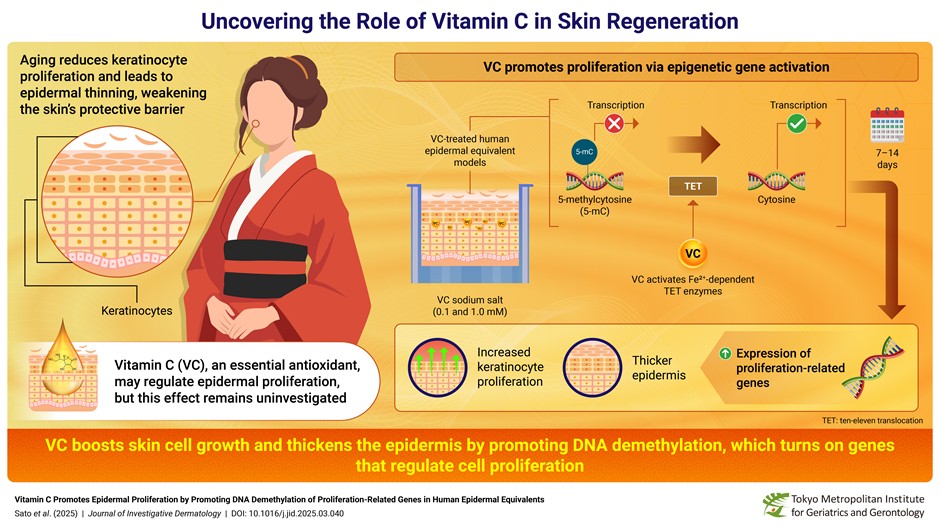
This happens because cell production in the epidermis, the outermost layer, slows down. The result is a skin that feels less firm, heals more slowly, and shows signs of ageing more clearly.
But according to Dr Akihito Ishigami, the vice president of the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Geriatrics and Gerontology (TMIG), vitamin C may help reverse this process at the genetic level.
Working with colleagues from Hokuriku University and ROHTO Pharmaceutical, Dr Ishigami’s team discovered that vitamin C encourages keratinocytes, the main type of skin cells, to divide and multiply. The result: a thicker, healthier epidermis.
How it works: Reawakening skin’s genetic memory
To study vitamin C’s effects, researchers used 3D human skin models that mimic how real skin behaves.
They applied vitamin C at levels similar to what the body naturally delivers through the bloodstream.
Within a week, they noticed a clear difference: the inner layers of skin became thicker, while the outermost dead layer remained unchanged. After two weeks, the effect was even more pronounced.
So, what was happening beneath the surface?
Vitamin C was found to trigger DNA demethylation, a biological process that switches genes on. Over time, our skin’s growth-related genes can become “silenced” by chemical tags called methyl groups.
Vitamin C helps remove those tags, reactivating the genes that tell skin cells to grow, divide, and renew.
This process relies on enzymes known as TET enzymes, which vitamin C fuels by restoring the iron they need to function; without this, the genes stay off, and the skin stays thin. Which often leads to sagging and wrinkles.
The results
The researchers identified more than 10,000 regions of DNA that were affected by vitamin C, leading to up to 75-fold increases in cell growth gene expression.
When they blocked the TET enzymes, these effects vanished, and this now confirms that the vitamin C’s impact is both real and deeply biological.
For ageing adults or people with damaged skin, this discovery could change how we think about skincare, not as surface-deep, but as a way to support natural regeneration from within.
What does this mean for your skincare routine?
If vitamin C is not already part of your routine, now might be the time to consider it.
Whether through topical serums or dietary supplements, the study suggests that vitamin C doesn’t just help skin look better, it helps it be better.
And while more research is needed to fine-tune the most effective delivery methods, the message is clear: vitamin C is more than a glow-up; it is a cell-level reboot.
"Our findings show that vitamin C helps thicken the skin by encouraging keratinocyte proliferation through DNA demethylation," says Dr. Ishigami.
"It makes vitamin C a promising treatment for thinning skin, especially in older adults."
So the next time you apply a vitamin C serum or enjoy your morning citrus, remember—you’re not just enhancing your glow; you could be helping your skin rebuild and renew itself from within.
Top Stories Today














































